Plan the enterprise hierarchy
Plan your hierarchy before you use the tool. After you save your changes you cannot change the hierarchy.
The Enterprise Migrator tool displays the organizations currently in your
BlackBerry AtHoc
system. By default, new organizations that are created in the system are listed under the System Setup node. These are standalone enterprise organizations. They can be used as either an enterprise organization or moved under an enterprise to become a suborganization.In an
AtHoc
enterprise, there are three levels:- The top level is System Setup. The System Administrator role manages the system by logging into the System Setup organization. User attributes and alert folders can be created here, which all organizations in the system inherit.
- The next level is Enterprise. There can be multiple enterprise organizations associated with System Setup. The enterprise administrator manages the enterprise organization and suborganizations. The administrator can create enterprise-level attributes and folders for the enterprise organization that is inherited by its children.
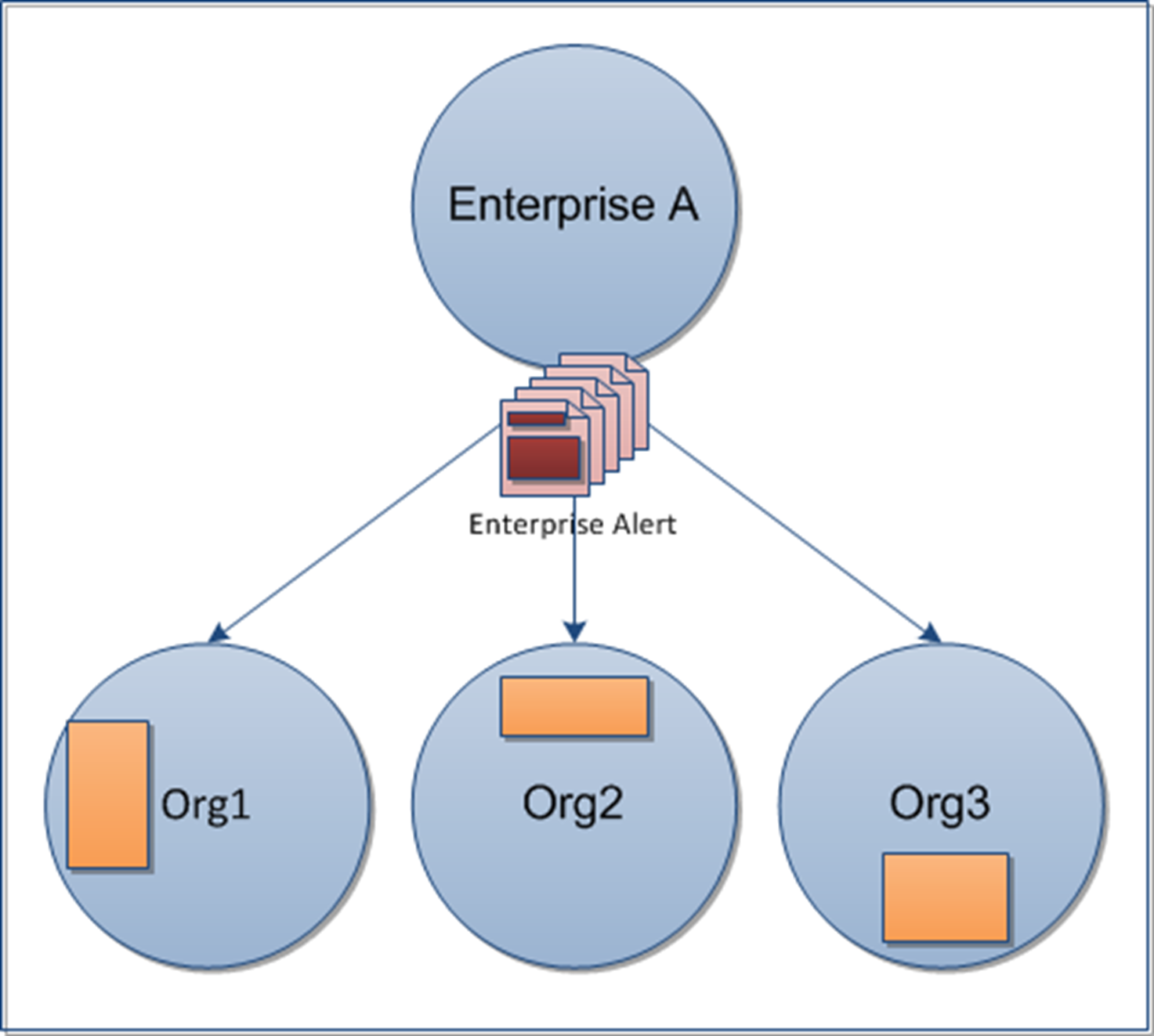
- The third level is suborganization (or member organization). Each enterprise organization can have a unlimited number of suborganizations. The organization administrator manages the local organization only. The administrator can create organization-level attributes and folders for the local organization. A suborganization has peers, but no children.
Using the migration tool, you will choose one organization that acts as the Enterprise organization, and the rest that are members (suborganization). System Setup is the default and top-level organization. An enterprise organization inherits from System Setup and a suborganization inherits from the enterprise organization.
- Typically, content is managed at the Enterprise level because it provides one place to control the content and send alerts to all users in suborganizations. The suborganization level contains content specific to a subset of the Enterprise, customized for a particular organization.
- The Enterprise Migrator tool migrates existing operators that have an Enterprise Administrator role in a suborganization to Organization Administrator. Other operator permissions remain unchanged.
- When you move an organization into the Enterprise, the connect relationships and user accounts remain unchanged for the organization.
Enterprise hierarchy uses inheritance for user attributes and alert folders. Content created at the system level can be seen by Enterprise and suborganizations, but not edited. Content created at the suborganization level cannot be seen at the Enterprise or system levels.